Web 3.0 is the next step in the evolution of the internet and aims to make the web a smarter, decentralized and transparent place.
In this article, we are going to be taking a look at the three stages of the Evolution of the Web, known as Web 1.0, Web 2.0 and Web 3.0. Then, we will understand the features and advantages of Web 3.0.
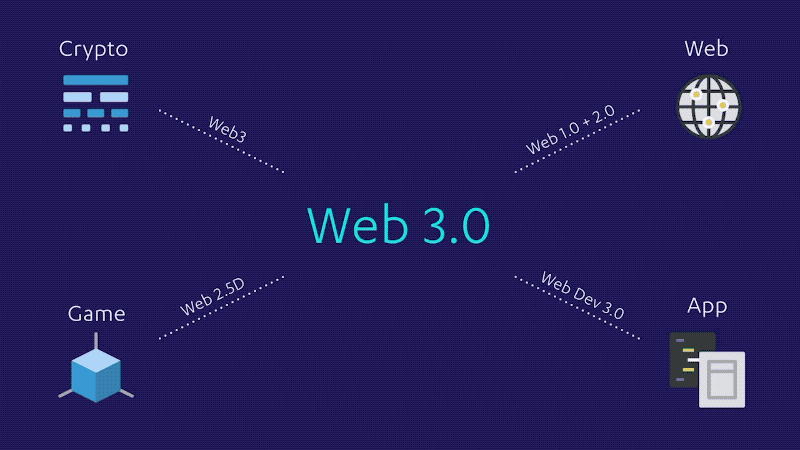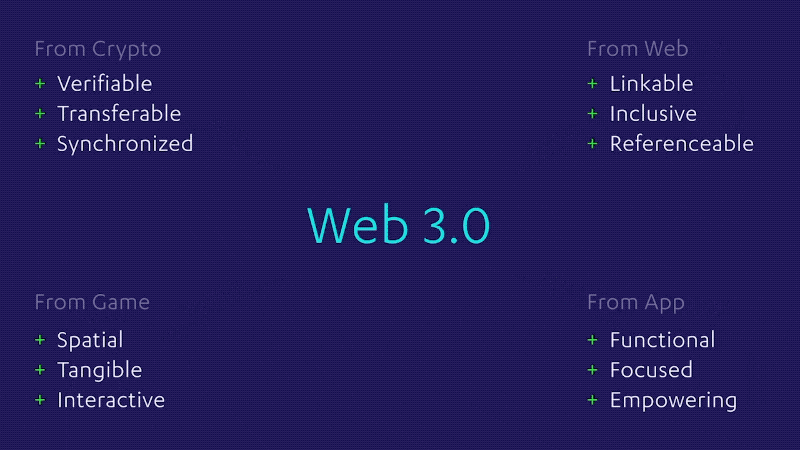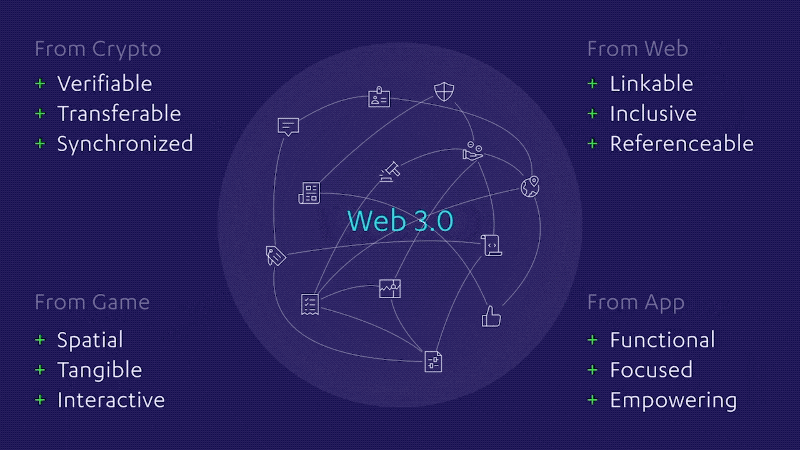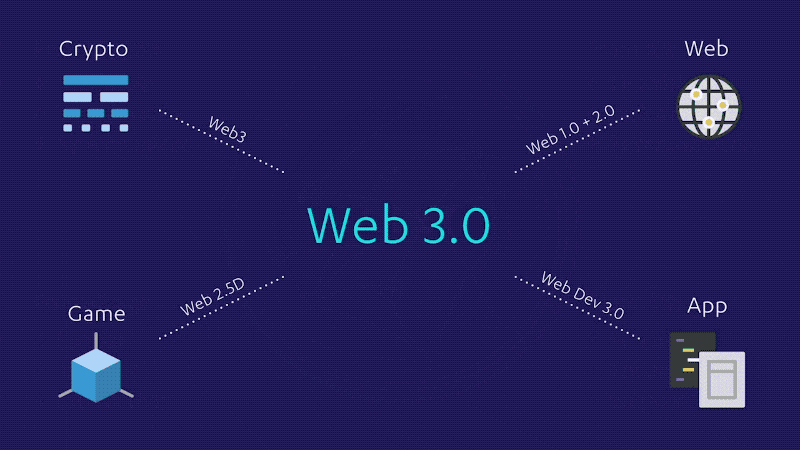
The Evolution of Web
The web, as we know it today, is completely different from what it used to be in its early days. The evolution of the web is mainly partitioned into three distinct stages: Web 1.0, Web 2.0, and Web 3.0.
Before understanding Web 3.0, let us first take a deeper look at its predecessors.
Web 1.0
Web 1.0 was the first ever iteration of the World Wide Web. It lasted approximately from 1991 to 2004. The websites from this era were static and didn't have any interactivity at all. These websites contained information served up in either text or image format.
Hence, Web 1.0 is also known as read-only web.
Web 2.0
Web 2.0 , the second iteration of the World Wide Web, is the web marked by the change from static to dynamic content, as well as the rise of social media. Some Web 2.0 application examples include video sharing sites like YouTube, web hosts like WordPress and social networking like Facebook and Instagram. Web 2.0 is also known as the read-write web.
Web 3.0
It is the third iteration of the World Wide Web, also known as the read-write-execute web. This era of the web has technologies like Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning at its core.
Unlike Web 2.0, Web 3.0 applications don't usually run on a single server or store their data in a single database. Instead, Web 3.0 applications run on blockchains, and are called DApps (decentralized apps).
Wolfram Alpha and Apple's Siri are two examples of web 3.0 applications.

Features of Web 3.0
The following are the defining features of web 3.0 :-
Decentralization
This is the core property of Web 3.0. Unlike Web 2.0, which stores information at fixed location, generally on a single server, Web 3.0, where information would be found based on its content, it could be stored at multiple locations simultaneously and hence be decentralized.
This breaks down the massive databases currently held by tech giants like Google, and prevents their undue enrichment by handing greater control to the users.
Trustless
Web 3.0 allows participants to interact directly without going through a trusted intermediary, making it trustless. In addition, this web is also permission-less as anyone can participate without authorization from a governing body.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
In Web 3.0 computers understand information similarly to humans, thanks to technologies based upon Semantic Web concepts. With the help of machine learning, Web 3.0 is constantly improving its accuracy, as ML uses data and algorithms to imitate how humans learn.
Connectivity
With Web 3.0, information and content are more connected and ubiquitous, accessed by multiple applications and with an increasing number of everyday devices connected to the web.

Advantages of Web 3.0
One of the Web 3.0's major advantage is that it solves one the most serious issues of Web 2.0, which is the gathering of personal data by private networks. In the past, this data has been subsequently sold to marketers or even stolen by hackers. Being decentralized, Web 3.0's network is not controlled by a single organization.
Apart from this, some other advantages of Web 3 include: expanded data connectivity, more productive web perusing, more accurate search results, better showcasing, easier sharing of knowledge, and compelling correspondence.

